Current Transducers: Enabling Precise Current Measurements for Enhanced Electrical Systems
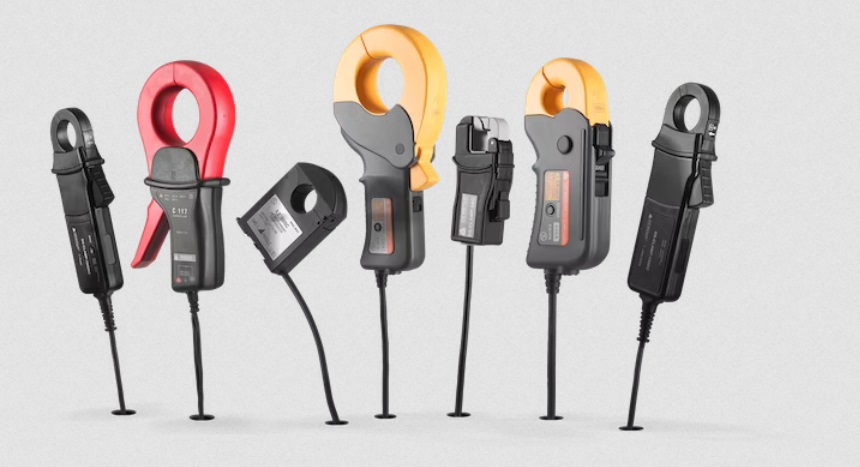

Current transducers serve as the bridge between the physical realm of electrical currents and the digital domain of measurements and control. They enable the conversion of current signals into proportional electrical signals that can be readily processed, monitored, or fed into control systems.
By providing accurate and reliable current measurements, these devices are instrumental in optimizing energy consumption, preventing equipment failure, and ensuring the overall safety and stability of electrical systems.
In the realm of electrical engineering and power systems, accurate current measurement plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient and safe operation.
Current transducers, also known as current sensors or current transformers, have emerged as indispensable devices that facilitate precise current monitoring in various applications.
This article delves into the significance, working principle, and diverse applications of current transducers, shedding light on their vital role in enhancing electrical systems.
Working Principle of Current Transducers:
Current transducers operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The conductor carrying the current to be measured passes through the primary winding, generating a magnetic field around it.
This magnetic field induces a proportional current in the secondary winding, allowing for non-intrusive and galvanically isolated measurement.
The secondary current or voltage signal can then be utilized for further analysis, control, or monitoring.
Applications of Current Transducers:
- Power Distribution and Energy Management: Current transducers play a vital role in power distribution systems, helping to monitor and control current levels in electrical grids, substations, and switchgear. They enable accurate load balancing, fault detection, and real-time energy management, contributing to optimized power distribution and improved system efficiency.
- Motor Control Systems: In motor control applications, current transducers provide crucial insights into the operating conditions of motors. By measuring the current flowing into the motor windings, these devices aid in motor protection, performance optimization, and fault diagnosis. They are commonly used in industrial automation, robotics, and HVAC systems.
- Electrical Testing and Monitoring: In testing and monitoring equipment, current transducers provide accurate measurements for quality assurance, safety compliance, and diagnostics. They are utilized in electrical testing laboratories, power quality analyzers, and equipment for insulation testing and ground fault detection.
- Electrical Safety Systems: Current transducers are integral components of electrical safety systems such as residual current devices (RCDs) and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs). By continuously monitoring the current imbalance between the live and neutral conductors, these devices offer protection against electrical shocks and fire hazards.
current transducer have revolutionized the field of current measurement, enabling accurate, non-intrusive, and galvanically isolated monitoring in a wide range of electrical applications.
Their precise measurements and reliable performance contribute to enhanced system efficiency, optimal energy management, and improved safety.
As technology advances and electrical systems become more sophisticated, current transducers will continue to play a pivotal role in ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of our increasingly electrified world.